Java Beginner: Lesson 9 - switch
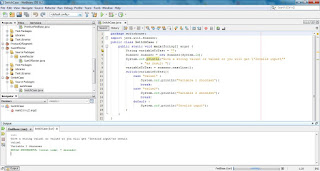
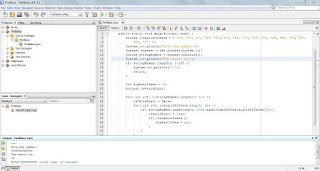
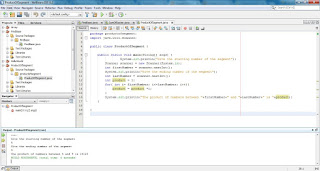
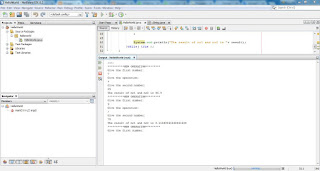
In this lesson we will cover the switch statement. The switch statement same as if statement is a conditional statement, so it checks if a condition is fullfilled, but differently from if statement it is used for a well known set of values and for specific variables. If statement can be used to test complex conditions which can involve even more than one variable, while the switch statement is used to check the value of a specific variable. Example code: switch(variableToTest){ case "value1" : System.out.println("Variable 1 choonsen"); break; case "value2": System.out.println("Variable 2 choonsen"); break; default : System.out.println("Invalid input"); } The example code above shows the structure of a switch statement in case we would test a string variable. So if the string variable with name ...